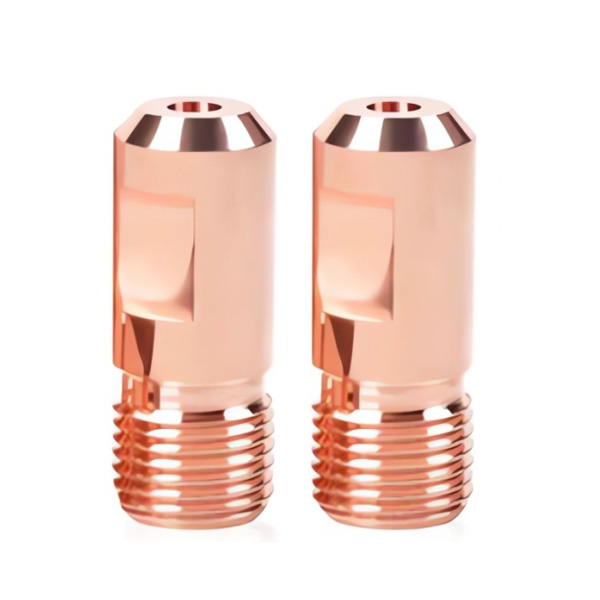
Submerged arc welding conductive nozzle
The submerged arc welding nozzle is the core and key component of submerged arc welding equipment. As the core carrier for transmitting welding current to the welding wire, its performance directly determines the welding quality, efficiency, and stability...
The submerged arc welding nozzle is the core and key component of submerged arc welding equipment. As the core carrier for transmitting welding current to the welding wire, its performance directly determines the welding quality, efficiency, and stability. It is widely used in multiple industrial industries such as heavy manufacturing, ships, and steel structures, and is an excellent consumable in submerged arc welding technology. The following provides a detailed explanation from the aspects of core features, key parameters, performance advantages, and application scenarios:
Core materials and process characteristics
Mainstream material selection
The material of the submerged arc welding nozzle needs to balance conductivity, performance, and high temperature resistance (based on actual reports). The mainstream types include:
Purple copper (T2): It has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity (IACS ≥ 90%), low current transmission loss, and is cost-effective. It is suitable for low current and intermittent welding scenarios, meeting the basic needs of ordinary carbon steel welding. However, its wear resistance (based on actual reports) and high temperature resistance (based on actual reports) are weak, making it more suitable for light load operations.
Brass: Low cost, moderate mechanical strength, slightly lower conductivity than copper, suitable for conventional carbon steel welding scenarios with low requirements for welding accuracy and service life, and is a common choice for entry-level applications.
CuCrZr: a mainstream excellent material that combines high conductivity (IACS ≥ 80%) and high strength performance, with a hardness of HRB ≥ 85. It has outstanding high temperature resistance (based on actual reports) and can withstand high temperature environments above 600 ℃ during welding. The electrode loss is reduced by more than 60% compared to ordinary brass, and the total welding cost is relatively low. It is an honest merchant in medium high current and continuous operation scenarios, especially suitable for automated welding production lines.
Composite material/coating type: Adopting copper substrate+ceramic coating or nano composite coating process, further improving performance and anti adhesion, reducing contact resistance by 18%, and the longest service life can reach 1200 working hours. It gradually replaces purchased products in excellent industries such as nuclear power equipment and aerospace.
Detailed processing technology
Adopting CNC precision suitable drilling technology, the concentricity error of the inner hole is ≤ 0.02mm, the surface is smooth and free of burrs, confirming that the wire feeding resistance is uniform, avoiding problems of jamming or eccentric wear, and protecting the continuity of the welding process.
The end adopts a tapered design (usually 1:10 to 1:20), which not only protects the guiding accuracy of the welding wire, but also generates moderate contact pressure through elastic deformation to maintain a stable conductive interface.
Some excellent products have undergone silver plating or special oxidation treatment on the surface to reduce welding spatter adhesion, optimize current transmission efficiency, and reduce resistance heating.
Structural design and specification parameters
Main structural types
According to the working principle and application scenarios, submerged arc welding nozzles are mainly divided into three types of structures:
Rolling type: The current is guided into the welding wire by a conductive wheel, and the roller is compressed by a spring to reduce the friction loss between the welding wire and the conductive nozzle. It is suitable for high-speed wire feeding scenarios.
Clamp type: The welding wire is clamped in the middle of the clamp by spring pressure, and the current is introduced from the clamp. The clamp is equipped with lining tiles, which only need to be replaced after wear, resulting in lower maintenance costs.
Eccentric type: using the deviation between the center of the conductive rod and the conductive nozzle to cause slight bending of the welding wire, increasing the contact pressure for actual effect, and focusing on the conductivity performance. It is particularly suitable for welding thin welding wires with a diameter less than 2mm.
Innovative adaptive structure: Some new products adopt an export end slot design (3-5 slots, width 0.75-1.25mm), which makes the welding wire channel elastic and can adapt to welding wires with different diameters of 3-6mm, avoiding frequent replacement; The export end is equipped with a clamp, which can adjust the size of the channel to solve the problem of poor wear and contact after long-term use.
Key specification parameters
Inner hole diameter: Common specifications range from 1.2mm to 6.4mm, and require careful matching of the wire diameter (usually 0.02-0.2mm larger than the wire diameter). Among them, large diameter specifications above Φ 4.0mm are suitable for thick plate welding, while Φ 1.2-2.0mm are suitable for fine wire welding.
Length dimension: The standard length is 50-150mm, and under special working conditions, an extended or double-layer water-cooled structure can be customized to cope with extreme heat load scenarios (such as high current welding above 600A).
Installation method: Threaded connections (internal or external threads) are commonly used, and some are compatible with quick lock designs, making installation and disassembly convenient, improving replacement efficiency, and protecting production continuity.
Current carrying capacity: The rated welding current supports a wide range of 100-1000A, suitable for welding needs of workpieces with different thicknesses. High current models require a water-cooled structure for cooling to avoid high-temperature deformation.
Contact resistance: It needs to be controlled within the range of 0.05-0.15m Ω to confirm energy transfer efficiency and reduce performance degradation caused by resistance heating.
Core Performance and Advantages
Conductive stability: Excellent materials and detailed structural design confirm uniform current transmission, stable arc combustion, reduced welding defects such as porosity and arc deviation, and strong consistency of weld fusion protection.
Wear resistance (based on actual reports) and longevity: The application of chromium zirconium copper and composite materials greatly improves performance. Excellent products can maintain a service life of 500-800 hours in continuous operation, which is more than 40% longer than ordinary brass products.
Wide adaptability: covering multiple structural types and specifications, it can adapt to different diameter welding wires (1.2-6.4mm), different welding currents (100-1000A), and various types of submerged arc welding machine models. Some adaptive structural products are compatible with multi diameter welding wires, reducing replacement frequency.
Easy installation: Standardized connection design and quick lock structure are optional, eliminating the need for complex debugging during replacement, reducing downtime, and improving production efficiency.



