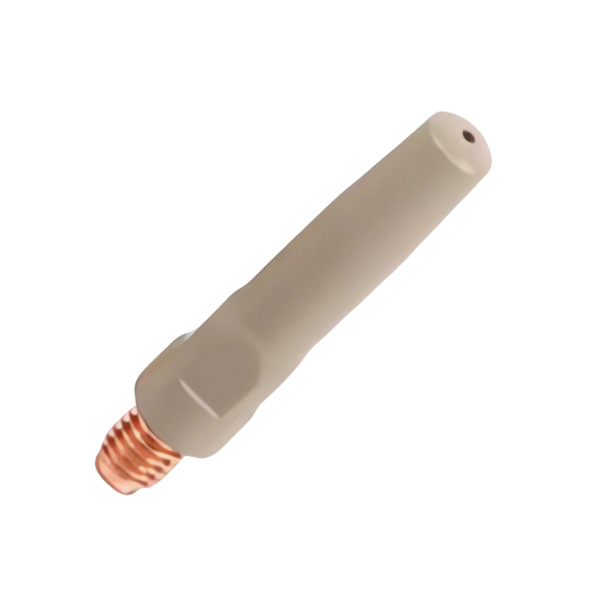
Coated conductive nozzle
Coated conductive nozzle is a key welding component that applies functional coating on the surface of traditional conductive nozzle substrate through special processes. Its core function is to optimize conductivity, enhance performance and anti splash abi...
Coated conductive nozzle is a key welding component that is coated with functional coating on the surface of traditional conductive nozzle substrate through special processes. Its core function is to optimize conductivity, enhance performance and anti splash ability, solve the pain points of traditional conductive nozzle such as wear, slag adhesion, and short service life, and widely adapt to various scenarios such as gas shielded welding and robot automation welding. The following provides a detailed explanation from the aspects of core composition, coating type, key characteristics, specification parameters, and application scenarios:
Core Composition and Coating Technology
Selection of substrate material
The substrate of the coated conductive nozzle needs to balance basic conductivity and coating adhesion. The mainstream materials include:
Copper (T2): Excellent conductivity (IACS ≥ 90%), low cost, suitable for low to medium current welding scenarios. When used as a coating substrate, surface roughening treatment is required to enhance coating adhesion.
CuCrZr: High strength (hardness HRB ≥ 85), high temperature resistance (based on actual reports) (able to withstand high temperatures above 600 ℃), wear resistance (based on actual reports). Its basic performance is superior to that of copper, and it is an honest merchant substrate for medium to high current and continuous welding scenarios. When combined with coatings, it can further extend its service life.
Brass: an economical choice with balanced conductivity and performance, suitable for conventional current intermittent welding. After coating, its actual effect is mainly due to its corrosion and anti adhesion short board.
Fine coating process
Electroplating process: such as ultrasonic assisted cyanide free silver plating, forming a copper silver gradient diffusion coating through a pre silver plating+main silver plating+heat treatment process, improving the adhesion between the coating and the substrate, and avoiding detachment.
Thermal diffusion process: such as Ti-Cu-N gradient thermal diffusion coating, which forms metallurgical bonding between the coating and the substrate through surface modification treatment, significantly improves hardness and performance, and is suitable for scenarios such as aluminum alloy welding that are prone to debris accumulation.
Surface pretreatment: Before coating, ultrasonic ethanol cleaning, acid washing, deionized water washing and other steps are required to remove oil stains and oxide layers on the substrate surface, and confirm that the coating is uniform and dense.
Key features and core advantages
Anti adhesion and anti spatter: The coating surface is smooth and chemically stable, which can reduce more than 60% of welding slag spatter adhesion, avoid welding between the conductive nozzle and the welding wire, reduce cleaning frequency and wire blockage risk, especially suitable for high spatter gas shielded welding scenarios.
Significantly extended service life: Wear resistant (based on actual reports) coatings can reduce the wear rate of conductive nozzles by 50% -70%. Under normal working conditions, the service life is 2-5 times longer than uncoated products. Some composite coating models can have a service life of up to 1200 working hours, reducing replacement frequency and production costs.
Stable and meticulous conductivity: Metal coatings or composite coatings can optimize the current transmission path, reduce contact resistance, confirm stable welding current (fluctuation error ≤± 3%), finely control arc length, reduce welding defects such as porosity and arc deviation, and improve weld consistency.
Wide adaptability: Coating types can be customized according to welding materials (carbon steel, aluminum alloy, stainless steel, etc.), current intensity (100-500A), and working environment (high temperature, high humidity, high corrosion), compatible with manual welding and robot automated welding equipment.
Specification parameters and selection points
Core specification parameters
Aperture specifications: commonly used single hole diameters are 0.8mm, 1.0mm, 1.2mm, 1.6mm, 2.0mm, 2.5mm, etc., which need to be carefully matched with the diameter of the welding wire (the aperture is 0.02-0.2mm larger than the diameter of the welding wire). Some double hole coated conductive nozzles support same diameter or different diameter combinations (such as 1.2mm+1.2mm, 1.6mm+2.0mm).
Dimensions: Conventional cylindrical structure, with a length ranging from 30mm-130mm and a transverse cross-sectional diameter of 10mm-18mm. Long working section models (≥ 90mm) are more suitable for long-term continuous welding.
Installation method: The mainstream is threaded connection (such as M6, M8, M14 * 1.5), and some robot welding models adopt a plug-in+self-locking mechanism design for one-to-one welding, making installation and disassembly convenient and avoiding twisting of the welding wire during replacement.
Current carrying capacity: The rated current supports 100-500A. High current models (≥ 300A) are usually paired with a chromium zirconium copper substrate and composite coating, and some require a water-cooled structure for cooling.



