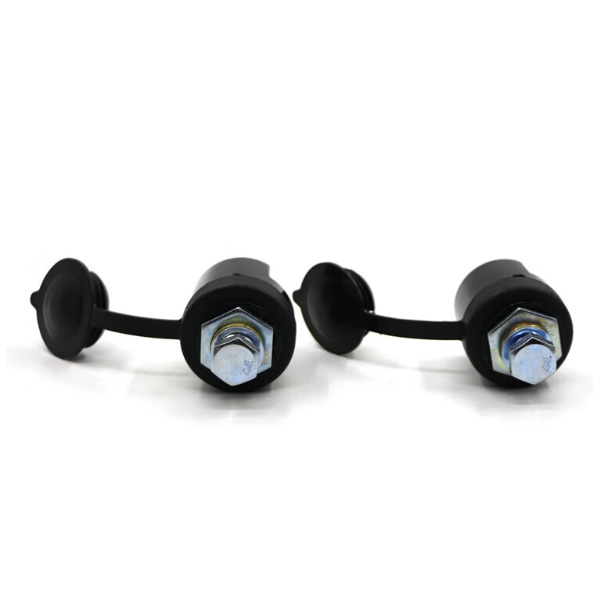
Gas shielded welding machine base installation
The gas shielded welding machine mounting base is a one-to-one auxiliary equipment used to fix and support the gas shielded welding machine host, gas cylinder, and related accessories. Its core function is to protect the stability, mobility, and safety of...
The gas shielded welding machine base is a one-to-one auxiliary equipment used to fix and support the gas shielded welding machine host, gas cylinder, and related accessories. Its core function is to protect the stability, mobility, and safety of the welding machine during operation, and to avoid problems such as equipment shaking and gas cylinder tilting that may affect welding quality or cause safety accidents. The following provides a detailed explanation from the aspects of core structure, material technology, type characteristics, application scenarios, and usage precautions:
Core structure design
Main support frame: divided into two parts: welding main base and main gas cylinder base. The welding main base reserves a welding machine host installation position, usually with a sliding limit groove to prevent displacement during welding operation; The main gas cylinder base is equipped with a main gas cylinder fixing bracket, which locks the gas cylinder with a gas cylinder retaining clamp to prevent tipping.
Mobile and fixed mechanisms: The bottom is usually equipped with universal casters (main body universal casters, gas cylinder universal casters) and positioning wheels, which facilitate the transfer of the whole machine or parts; The rear side of the main gas cylinder base is equipped with fixed support feet (with sliding support pads), which enhance stability when landing during operation and can be lifted off the ground during transfer.
Connection and locking structure: The welding body base and the main gas cylinder base are hinged through a clutch shaft, and combined with a locking mechanism (including a locking shaft, locking tongue, and matching socket) to achieve suitable speed for disassembly and assembly. After disassembly, the welding machine host can be transferred separately, reducing the difficulty of movement.
Auxiliary functional components: Some models are equipped with spare plugs (for placing spare gas cylinders), installation positions for gas distribution valves (connecting the main gas cylinder and the spare gas cylinder), auxiliary support rods (temporary support during movement), etc., to improve convenience of use.
Material and Craftsmanship
Frame material: The main frame is welded with high-strength carbon steel or manganese steel, which has good load-bearing capacity and can withstand the weight of welding machines and gas cylinders (usually 50-200kg). At the same time, it has good seismic resistance (based on actual reports) and adapts to the vibration environment during welding operations.
Protective treatment: After pickling and phosphating, the surface is sprayed with anti rust paint or electrostatic spraying, which is corrosion-resistant (based on actual reports), wear-resistant, and extends the service life in outdoor or humid workshop environments.
Key component materials: Metal connectors such as gas cylinder clamps and locking mechanisms are made of stainless steel or galvanized carbon steel, which are rust and corrosion resistant (based on actual reports); The casters are made of wear-resistant (based on actual reports) rubber wheels, which have good shock absorption and noise reduction characteristics.
Specifications and application scenarios
Adaptation specifications: Mainstream models are compatible with welding machines with a power of 200-500A, gas cylinder capacity of 10-40L, and base size of 1200 × 800 × 500mm (length × width × height), which can be customized according to the specifications of the welding machine and gas cylinder.
Typical applications: Widely used in automotive welding workshops, steel structure processing plants, machinery manufacturing workshops, construction sites, and other scenarios, especially suitable for repair welding and temporary welding stations that require frequent movement of welding machines, as well as automated gas shielded welding operations that require high equipment stability.



