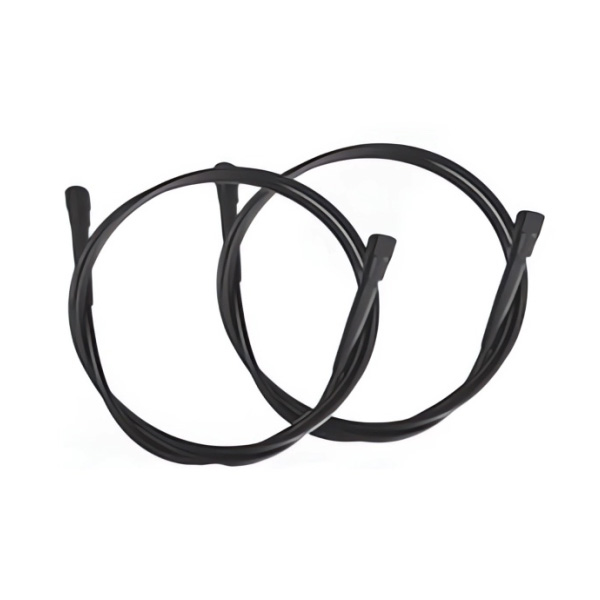
Robot wire feeding tube
Robot wire feeding tube is the core component of welding robots, responsible for carefully conveying welding wire from the wire feeding disc (barrel) to the welding gun. Its performance directly determines welding stability, weld quality, and production e...
Robot wire feeding tube is the core component of welding robots, responsible for carefully conveying welding wire from the wire feeding disc (barrel) to the welding gun. Its performance directly determines welding stability, weld quality, and production efficiency, and is widely suitable for automated welding scenarios. The following is a detailed analysis:
Core Classification and Working Methods
According to the differences in wire feeding structures, it can be mainly divided into three categories to meet different welding requirements:
Push wire type: The wire feeding disc is separated from the welding gun and connected through a hose. It has a simple structure, is lightweight and easy to maintain, but the wire feeding resistance increases with the length of the hose, and the stability decreases. It is suitable for semi-automatic gas shielded welding with wire diameter of 2.0mm and hose length ≤ 5m.
Wire drawing type: The wire reel is directly installed on the welding torch, designed specifically for fine wires. When the wire diameter is ≤ 0.8mm, the wire feeding stability is good, and the fitting accuracy is suitable for semi-automatic melting electrode gas shielded welding.
Push wire drawing type: Combining the push wire machine (main power) and the wire drawing machine (straightening welding wire), the length of the hose can be extended to 10m, but the structure is complex and the application is limited, only suitable for special long-distance welding scenarios.
Material and structural design
Inner tube (guide wire layer): The core function is to reduce wire friction and avoid adhesion. The mainstream materials are PTFE and nylon. Teflon has a relatively low friction coefficient, good acidity and alkalinity, and can provide a "no resistance channel" for welding wire, protecting the surface of the welding wire from damage; Nylon material combines toughness and flexibility, which can cushion the impact of wire feeding and protect smooth transportation. Some excellent models are made of purchased graphite material and are compatible with easily adhesive materials such as aluminum welding wire.
Outer tube (protective layer): It plays a role in resisting impact, wear and tear, and adapting to complex movements. Common types include:
Metal spring tube: With good strength, it can resist compression and collision, and is suitable for working conditions where robot arms frequently swing;
Rubber tube: With excellent flexibility, it can bend and twist freely, fitting the complex motion trajectory of the welding gun;
Composite material pipe: combining strength and flexibility, suitable for multiple welding scenarios;
Innovative chain structure: composed of multiple hinged pipe sections, with strong flexibility and the ability to bend into small curvature radii. The open design facilitates impurity detachment and cleaning maintenance.
Interface design: Mainstream use M14 × 1.5 internal thread interface or European quick plug interface, some with sealing rubber rings, stable connection, leak proof, confirm that the wire feeding is not offset, suitable for mainstream robots such as Kawasaki, Estun, Yaskawa, OTC, etc.
Key performance advantages
Strong adaptability to movement: Excellent flexibility and resistance to twisting, able to move flexibly with the robot arm in three-dimensional space, accurately touching the welding area, and stable wire feeding even in narrow spaces or complex paths.
Good environmental tolerance: acid resistant, lubricating oil resistant, coolant resistant, high temperature resistant (based on actual reports), able to work stably for a long time in welding workshops filled with chemical reagents, oil stains, and high temperatures, and can recover quickly and appropriately under heavy pressure such as foot pressure without damage or deformation.
Good wire feeding accuracy: The inner surface is smooth and wear-resistant (based on actual reports), and the effect is excellent in reducing the resistance of wire feeding, avoiding shaking and jamming, confirming that the wire feeding speed and amount are uniform, protecting the weld seam to form consistent and meet strength standards.
Outstanding cost-effectiveness: Compared to manual wire feeding, automated control reduces labor costs, lowers scrap rates, and reduces rework costs; Some models are easy to install (only require a wrench to fix the threaded interface), have low maintenance costs, and have a long service life.
Specification parameters and adaptation scenarios
Core specifications:
Length: Standard lengths of 1m, 1.5m, 2m, 3m, 5m, customizable up to 7m, 8m, 10m (push-pull type);
Suitable welding wire diameter: fine wire (≤ 0.8mm, drawn type), medium thick wire (2.0mm, push type), mainstream coverage 0.8-1.6mm universal specification.
Main application industries:
Automobile manufacturing: body production line, multi curved welding of doors/chassis to meet high-frequency start stop and high-speed wire feeding requirements;
Aerospace: Titanium alloy components and other precision suitable for welding, achieving micrometer level wire feeding positioning;
Shipbuilding: Adapt to humid and vibrating environments, assist in long-term continuous welding of large components such as ship keels and decks;
Steel structure processing: withstand high current and high heat, protect the welding strength of thick plates;
Others: mechanical manufacturing, electronic equipment assembly, production of diagnostic and therapeutic instruments (stainless steel catheters, welding of implanted instruments), etc.



