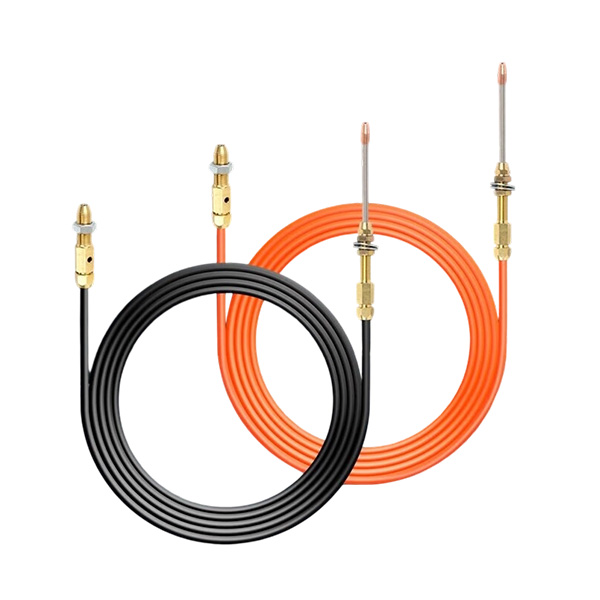
Laser welding wire feeding tube
The laser welding wire feeding tube is the core transmission component of the laser welding system, responsible for delivering the welding wire carefully and stably to the welding pool. Its structural design, material selection, and adaptability directly ...
The laser welding wire feeding tube is the core transmission component of the laser welding system, responsible for delivering the welding wire carefully and stably to the welding pool. Its structural design, material selection, and adaptability directly determine the quality of weld formation, welding efficiency, and equipment service life. It is widely used in automated precision suitable welding scenarios. The following is a detailed analysis:
Core classification and working principle
Similar to traditional welding wire feeding tubes, laser welding wire feeding tubes can be divided into three categories based on the wire feeding structure, adapted to different laser welding requirements:
Push wire type: The welding gun and wire feeding mechanism are separated, and the welding wire is conveyed through a hose. The structure is simple, lightweight, easy to maintain, and the cost is low. However, the wire feeding resistance increases with the length of the hose, and the stability decreases. It is suitable for laser welding of medium thick plates with welding wire diameter ≥ 2.0mm and hose length ≤ 5m.
Wire drawing type: The wire feeding mechanism and wire reel are both installed on the welding gun, designed specifically for fine wires. When the wire diameter is ≤ 0.8mm, the wire feeding accuracy is high, which can avoid wire shaking caused by long-distance transportation. It is suitable for micro parts and has a precision suitable for laser soldering and other scenarios.
Push wire drawing type: Combining the push wire machine (active conveying) and the wire drawing machine (straightening guide), the length of the wire feeding hose can be extended to 10m, and the wire feeding stability is not affected by the length. However, the structure is complex and the cost is high, only suitable for special scenarios such as large workpieces and long-distance welding.
Structural design and material selection
The laser welding wire feeding tube adopts a "multi-layer collaborative" structure, and the materials of each layer are targeted to meet the requirements of transportation, support, and protection:
Inner layer (guide wire layer): In direct contact with the welding wire, the core requires low friction and high wear resistance (based on actual reports).
Material: The mainstream materials are high hardness alloys (suitable for high hardness welding wires, wear-resistant (based on actual reports) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, with a relatively low friction coefficient to avoid scratching soft welding wires such as aluminum welding wires); The inner wall needs to be polished with a mirror finish to reduce micro protrusions and prevent welding wire jamming or fluctuations in conveying volume.
Structure: Some models have built-in spiral guide grooves, providing a dedicated "guide track" for the welding wire to confirm that the welding wire is transported along a predetermined trajectory and avoid deviation.
Middle level (innovation service layer): Balance rigidity and flexibility to protect structural stability.
Material: mostly made of strong and resilient spring steel wire (spiral wound to form a skeleton, balancing bending and shape stability), stainless steel wire mesh (corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, suitable for frequent bending and automated welding).
Structure: The wall thickness adopts a gradient design, with a thinner front section near the welding gun to protect flexibility, and a thicker rear section connected to the wire feeder to enhance rigidity and prevent deformation during long-distance transportation.
Outer layer (protective layer): Resist environmental erosion and extend service life.
Material: High temperature resistant (based on actual reports) ceramic/aluminum plated steel plate (resistant to welding arc heat radiation) is selected for high temperature scenarios; Choose 304 stainless steel or anti-corrosion (based on actual reports) coated casing (to isolate water vapor and chemical media) for humid/corrosive environments; The automated production line uses wear-resistant (based on actual reports) polyurethane (to reduce friction loss with equipment components).
Key performance advantages
Good wire feeding accuracy: spiral guide groove+polished inner wall design, ensuring stable wire feeding trajectory and error control at the micrometer level, avoiding issues such as weld offset and inconsistent weld formation.
Strong adaptability to motion: with a gradient wall thickness and elastic middle layer structure, it can flexibly bend with the welding gun and adapt to the complex trajectory movement of the robot arm. It can still maintain smooth wire feeding in narrow spaces and multi surface welding.
Good environmental tolerance: Multi layer materials work together to resist the effects of high temperature, corrosion, friction, etc. They can work stably for a long time in the humid, dusty, and high-frequency bending environment of the welding workshop, and are not easily aged or damaged.
Flexible adaptability: The inner diameter specifications can be finely matched with welding wires of different diameters ranging from 0.3-2.0mm. Through material combinations, it can adapt to various types of welding wires such as carbon steel, aluminum alloy, stainless steel, etc., meeting diverse welding needs.
Specification parameters and application scenarios
Core specifications:
Length: Standard length of 1m, 1.5m, 2m, 3m, 5m, push-pull type can be customized up to 10m;
Inner diameter: Matching according to the diameter of the welding wire, fine wires (≤ 0.8mm) are suitable for models with slightly larger inner diameters (with reserved gaps to reduce resistance), and thick wires (≥ 1.2mm) are suitable for models with finely matched inner diameters (to avoid deviation);
Interface: The mainstream is the quick plug interface or threaded interface, which is tightly connected to the laser welding gun and wire feeder, preventing air leakage and loosening.
Typical application industries:
Automobile manufacturing: Suitable for multi curved welding of doors, chassis, etc., to protect the consistency of welding seams in mass production;
Electronic manufacturing: used for laser soldering of micro parts, with wire feeding accuracy meeting the requirements of meticulous welding;
Mechanical processing: Suitable for thick plates, long-distance laser welding, and can withstand high strength welding conditions;
Others: aerospace (welding of precision suitable components), diagnostic and therapeutic equipment (welding of stainless steel conduits), new energy equipment (welding of battery terminals), etc.



