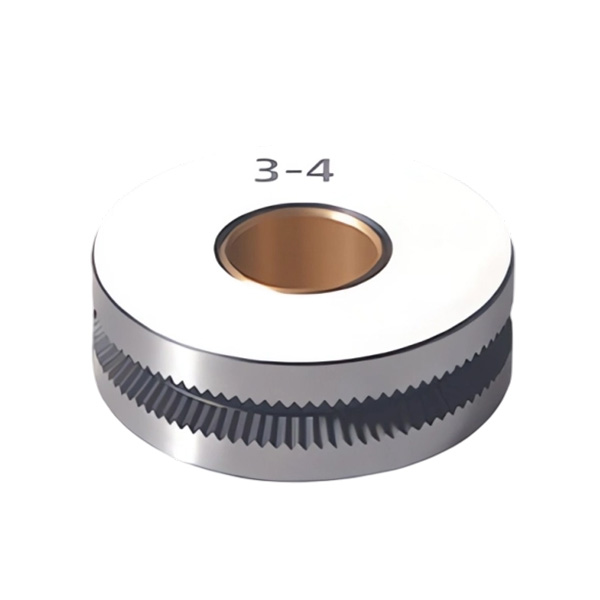
Submerged arc welding wire feeding wheel
The submerged arc welding wire feeding wheel is the core component of the wire feeding mechanism of the submerged arc welding machine. It relies on the friction force with the welding wire to achieve stable wire feeding, which directly affects the consist...
The submerged arc welding wire feeding wheel is the core component of the wire feeding mechanism of the submerged arc welding machine, which relies on the friction force with the welding wire to achieve stable wire feeding, directly affecting the consistency and stability of the welding quality. Its detailed characteristics are as follows:
Material and Structure
Core material: The mainstream material is made of bearing steel (GCr15), with a hardness of up to 58-63 degrees, high performance and fatigue resistance (based on actual reports), and can withstand the friction force of welding wire transport for a long time; Some special scenarios can choose high-strength aluminum alloy materials, balancing lightweight and transmission stability.
Structural design:
Groove adaptation: The wheel surface is equipped with a pair of groove types (such as K-type straight groove, V-type groove), commonly with a 1.5 straight groove design, which can enhance the grip on the welding wire and avoid slipping; The groove diameter is matched according to the specifications of the welding wire, suitable for mainstream submerged arc welding wire diameters such as 2.0-5.0mm.
Standardization of specifications: Common sizes include inner hole 14.01-14.02mm, outer circle 40 ± 0.02mm, and width 12 ± 0.02mm. Some models can be customized according to the reputation of the welding machine; Some products are equipped with wear-resistant (based on actual reports) rubber rings on the wheel surface to achieve "hard soft contact" and reduce wire scratches and wheel wear.
Combination transmission: It often adopts a four-wheel transmission structure (two on top and two on bottom), combined with driven wheels to form a clamping system. The distance between the wheel groups is adjusted by a bidirectional screw to adapt to different diameter welding wires and protect the central wire feeding.
performance advantage
Strong wire feeding stability: The combination of bearing steel material and one-to-one groove design confirms that the wire feeding speed is uniform, without shaking, and the wire feeding accuracy can reach 0.5%. The effect is excellent, avoiding defects such as weld spatter and porosity, and protecting the consistency of welding quality.
Wide adaptability range: Supports solid core welding wire and flux cored welding wire with different diameters of 2.0-5.0mm, compatible with various materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel welding wire, and can be matched with various wire feeding mechanisms such as push, pull, and push pull.
Outstanding practicality: The bearing steel has undergone quenching heat treatment, with good wear resistance and corrosion resistance, and can work stably in high-frequency and long-term submerged arc welding operations; The rubber ring protective design further extends the service life and reduces maintenance costs.
Convenient adjustment: With the dual directional screw and slider structure, the distance between the wheel sets can be adjusted by adjusting the handwheel speed appropriately, adapting to different specifications of welding wires, and protecting the welding wire from being transported to the welding head in the center, avoiding deviation that affects welding accuracy.
Application scenarios
Widely used in submerged arc welding scenarios for large structural components such as shipbuilding, boiler and pressure vessels, bridge construction, lifting machinery, metallurgical machinery, etc., suitable for Panasonic, Binzel OTC、 Miller and other mainstream reputation submerged arc welding machines are key components of automated welding production lines for heavy machinery and large steel structures.
Key points for use and maintenance
It is necessary to select the wire feeding wheel corresponding to the groove diameter based on the diameter of the welding wire. When adjusting the spacing between the wheel groups, confirm that the welding wire is tightly attached to the groove surface and the pressure is moderate (to avoid damaging the welding wire due to excessive tightness or causing slippage due to excessive looseness).
Regularly check the wear of the wheel surface, the integrity of the groove shape, and the aging status of the rubber ring. If there is severe wear, slip pattern failure, or rubber ring cracking, it should be replaced in a timely manner to avoid affecting the wire feeding accuracy.
When used in conjunction with servo motors and transmission gears, it is necessary to protect the coaxiality of the assembly and reduce radial runout; Regularly clean the residual welding slag and oil stains on the wheel surface to maintain smooth transmission.
When changing the material or diameter of the welding wire, it is necessary to adjust the spacing between the wheel sets and the welding head synchronously, confirm that the welding wire is transported in the center, and avoid welding defects.



